Most hemp connoisseurs recognize that organic growing practices result in higher-quality hemp flowers, and organic farming is more sustainable for the environment than conventional agricultural methods. However, we’ve found that some of our customers who are new to the world of smokable hemp aren’t exactly sure what the organic label represents.
Here at Cannaflower, we are committed to sustainable hemp cultivation and that is reflected in our product line which consists entirely of organic products. That’s why we wanted to take some of the mystery out of organic growing practices and labeling so that you can make an informed choice when you purchase hemp products. Let’s dive into the world of organic hemp.
What is Organic Hemp?
Hemp became a legal crop in the United States when Congress passed the Agricultural Act of 2018 and removed the plant from the list of controlled substances. The same piece of legislation, colloquially called the “Farm Bill,” also made hemp crops eligible to become certified as organic by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). The USDA defines organic agriculture as crops that have been “grown on soil that had no prohibited substances applied for three years prior to harvest.” Most synthetic fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides are forbidden to use in the hemp industry under the official USDA organic label.
Product labeling can be confusing. Hemp and CBD products (such as hemp protein powders, hemp seed oil, etc) labeled “natural” or “all-natural” are not the same as organically-certified products. The “natural” label generally means that the final product contains no artificial colors, flavors, or preservatives. The qualifications for earning the USDA-certified organic designation are far more stringent. The USDA strictly controls organically-certified hemp throughout the entire industrial hemp production and manufacturing process.
Regulations for Organic Hemp
The USDA appoints private, state, and even foreign organizations to make sure that organic farmers remain in compliance with federal organic regulations. Accredited agencies ensure that organic hemp farmers follow guidelines set out by the National Organic Program (NOP), including:
- New organic hemp growers must verify that the farmland has not been exposed to prohibited substances for three years prior to the first harvest. Farmers can verify what substances were used on the land by contacting the land’s previous owners and submitting the information to the accredited agency.
- Organic hemp must be grown without the use of prohibited synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. The NOP guidelines also prohibit farmers from using unnatural pest-control methods, such as irradiation. The USDA publishes a list of prohibited pesticides and fertilizers in a document called the National List of Allowed and Prohibited Substances, which organic farmers can consult online.
- The USDA prohibits organic farmers from using genetic engineering practices, and the use of genetically-modified organisms (GMOs) is not allowed in organic hemp products.
- In order to receive the USDA organic seal, manufacturers of hemp-derived products like CBD oils must prove that at least 95% of the ingredients qualify as organic. Products must also contain no ingredients that have been deemed harmful to human health or the environment.
Additionally, the NOP defines labeling requirements for organic hemp and hemp-derived products. Organic hemp product labels must list a complete ingredients list, including any inorganic ingredients and the percentage of inorganic ingredients.
Organic hemp farmers become certified by first choosing a local accredited organization and submitting an application and the appropriate fees to the agency. Organic hemp farms must outline their growing practices in detail on the applications. Once the overseeing agency approves of a farm’s application, the organization sends an inspector to ensure that the farm is actually adhering to the practices. If the accredited agency approves both the application and the inspector’s report, the farm is granted organic status through the USDA.
Each year, organic hemp farms undergo a thorough re-inspection in order to maintain their organic certification. Organic farms that violate USDA regulations face financial penalties or a complete revocation of their organic status.

The USDA also maintains a list of certified organic products permitted for use on organic farms. Products that follow the USDA guidelines for organic growing have a stamp from an overseeing agency, such as the Organic Materials Review Institute (OMRI). Many agricultural products that say “organic-based” on the label do not conform to USDA regulations.
Organic Hemp Farming Methods
Unlike conventional farming, organic farming uses no synthetic nutrients, herbicides, pesticides, or fungicides. Both indoor and sun-grown hemp flowers can be produced using organic methods.
Super Soil
Well-prepared soil is the foundation of healthy, organic hemp plants. Most hemp and cannabis growers call their soil “super soil.” Every experienced hemp gardener develops his or her own style of super soil using a range of ingredients, including:
- Organic materials such as coco coir or peat moss
- Compost made from vegetable matter
- Natural fertilizers like manure, bat guano, fish meal, and worm castings
- Microorganisms like mycorrhizal fungi and Trichoderma to strengthen the area around the roots
- Predatory mites to keep pests at bay
- Worms and nematodes
- Aerating ingredients such as perlite and rice hulls
Organic super soil has several advantages over other growing mediums. The natural organisms in the soil help to keep the pH in a suitable range. Organic gardeners in the US and Canada don’t need to flush their hemp plants to get rid of synthetic nutrients before harvesting.

Synthetic versus Organic Fertilizers
Imagine if your entire diet consisted of bottled vitamins with no vegetables, fruits, or any other actual food. That’s basically what conventional growers are doing with their hemp plants. Conventional fertilizers concentrate on three primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Synthetic NPK fertilizers use a process called chelation to force the plant’s roots to absorb the nutrients.
Conventional growers use synthetic fertilizers because they are immediately bioavailable, and they typically cost less. You may think of synthetic fertilizers as “fast food” for hemp plants. Like human fast foods, synthetic fertilizers carry a host of disadvantages over the long term, such as:
- It’s much easier to overfeed hemp plants with synthetic fertilizers.
- Synthetic fertilizers harm the health of the soil for future crops.
- Conventional NPK fertilizers allow salts and chemicals to build up in the soil and inside the hemp plants.
- Many synthetic fertilizers are made from petroleum products and other non-renewable resources.
Instead of synthetic fertilizers, organic farmers feed hemp with organic teas that help to enhance the microbial life around the plants. Organic fertilizers have many advantages over synthetics, such as:
- Organic fertilizers contribute to the health of the soil.
- It’s much harder to overfeed and “burn” hemp plants with organic nutrients.
- Organic fertilizers won’t contribute to salt or chemical build-up.
- Organic nutrients can be derived from sustainable sources.
The biggest drawback of organic fertilizers is that most are not immediately bioavailable. Organic hemp growers need to have patience and carefully compost nutrients so that microorganisms in the soil can release them and make them available to the plants. Organic growers also plant cover crops like clover to seal in nutrients.
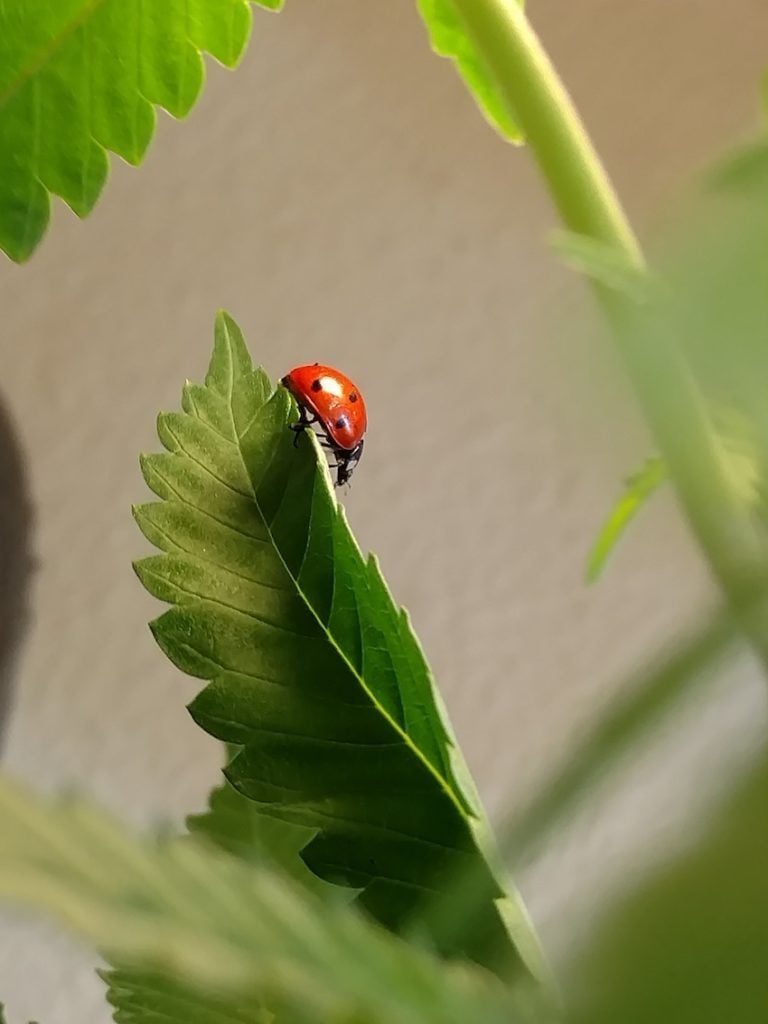
Organic Pest Control
Most organic hemp farmers will agree that the best defense against pests is to keep the plants healthy. That said, even the healthiest hemp garden may occasionally fall prey to common pests like spider mites and fungus.
Instead of blasting their crops with chemical pesticides, organic hemp farmers populate their gardens with beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and praying mantis. Organic farmers also amend the soil with predatory mites, such as P. persimilis and A. swirskii, that feed on harmful spider mites and mold.
To further repel damaging insects, organic hemp farmers regularly apply enzyme sprays and natural neem oil to hemp leaves.

How Does Growing Hemp Organically Improve Quality?
Now that we’ve discussed organic regulations and farming practices, you may be wondering what all of the extra work involved in organic hemp farming means to you—the consumer.
Taste
Most consumers agree that organic hemp flowers taste better than comparable strains grown synthetically. Growing hemp in rich, organic soil allows them to develop more complex terpene profiles. Terpenes are organic compounds that plants produce to attract pollinators and repel harmful insects. For us humans, terpenes are largely responsible for the flavor and aroma of our favorite agricultural goodies, including hemp flowers.
Additionally, organic hemp offers a smoother smoke because it doesn’t have residual chemicals from synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Chemical residues on synthetically-grown hemp and cannabis flowers have also been linked to adverse reactions like headaches and hangovers.

Potency
While genetics play a role in hemp plants’ cannabinoid content, organic hemp flowers are typically more potent than their synthetic peers. Organic soils contain many more beneficial nutrients than artificial solutions. Synthetic fertilizers concentrate on the basic NPK ratios to keep the plants alive with the possible addition of calcium and magnesium. Organic super soils offer hemp plants all of the basics plus many more nutrients that they require to thrive, including:
- Essential NPK macronutrients along with a fourth macronutrient: silicon
- Secondary macronutrients like sulfur, calcium, and magnesium
- Micronutrients, such as boron, manganese, iron, zinc, copper, molybdenum, nickel, and selenium
- Microorganisms that aerate the soil and provide many other benefits
Having access to the full range of nutrients and microbes means that organic hemp plants have everything they need to produce healthier leaves, more succulent flowers, and a thicker coat of trichomes full of cannabinoids like cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG).

Health
Most consumers choose to smoke hemp flowers because they’re looking for an enjoyable way to relieve stress and benefit from CBD. Some may be seeking a healthier alternative to smoking tobacco. Smoking synthetic hemp flowers laden with toxic chemicals is at cross-purposes with most consumers’ reasons for choosing hemp flowers in the first place.
Cannabis plants, including industrial hemp, are powerful bioaccumulators. They readily absorb any substance in the soil, including toxic chemicals. Conventionally-grown hemp uses synthetic fertilizers, which leave the flowers full of harmful substances like heavy metals and nitrates. Many of these substances are dangerous to consume and even more toxic to inhale. Just because a synthetic pesticide or fertilizer has been labeled safe for use on traditional agricultural crops doesn’t mean that the chemical won’t cause harm after being ignited and inhaled.

Yield
The quantity of hemp flowers harvested with each crop, typically called the yield, depends on several factors, such as:
- The genetics of organic hemp seeds
- The environment in which the plants were grown
- The techniques employed by the farmers
Switching to organic gardening may produce smaller yields at first. The initial lower yields may be discouraging for newly converted organic hemp farmers, but here at Cannaflower, we think the difference in quality is well worth the effort.
Organic hemp farming is both a science and an art. It takes time to build up exceptional quality organic soil. After organic farmers cultivate a high-quality microenvironment, they will be rewarded with yields as high or higher than synthetic farmers obtain. Moreover, organic farmers will have the pride and pleasure of sharing potent and delicious craft-quality hemp flowers with their customers.

Environmental Benefits of Organic Hemp
Organic Hemp Farming Helps Preserve the Soil
Soil erosion is a huge environmental problem resulting from conventional farming practices. Synthetic fertilizers and pesticides lead to depletion of the essential topsoil in conventional gardens. In contrast, organic hemp farming builds a fertile super soil that will be a precious resource for the farmer for many years into the future.
Organic hemp farming does much more than simply avoid depleting the soil. Hemp and other cannabis plants help to purify the soil through a process called bioremediation. While hemp’s tendency to absorb all the chemicals in the soil makes synthetically-grown flowers potentially harmful to smoke, the same tendency to be bioaccumulators makes organic industrial hemp crops useful for cleaning contaminated soil. Industrial hemp was even planted around Chernobyl to remove radioactive contamination from the nuclear disaster that occurred there.
Organic hemp farmers can clean the soil for the first few years by planting organic hemp to be used for industrial purposes before using the land for growing organic hemp flowers. After three years, the farmland may be eligible for USDA organic certification, and the farmer will have rich and fertile soil to start growing high-quality artisanal hemp flowers.
Organic Growing Conserves and Protects Water Sources
Organic gardening typically uses less water than conventional agriculture. Furthermore, chemicals used in synthetic gardening slowly build up and enter local water supplies. The build-up of toxic agricultural chemicals can contaminate water sources and make whole communities ill, including wildlife, livestock, pets, and humans.
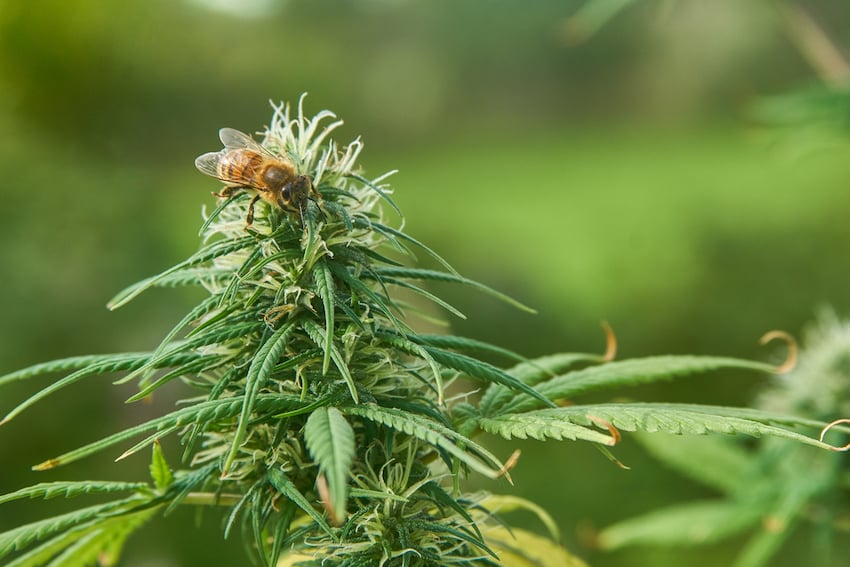
Organic Hemp Farming Helps Pollinators
Organic hemp fields provide habitat for bees and other helpful pollinators. A 2018 study done by Colorado State University found twenty-three different bee species in the hemp fields of northern Colorado.The bees can continue to thrive during the late summer and early fall when the number of other flowers dwindle.
Insects lack an endocannabinoid system, so bees don’t react to cannabinoids like CBD in hemp flowers. However, synthetic pesticides and fertilizers have a profoundly negative impact on bee populations. Without bees to pollinate plants, we would lose some of our most important crops, including apples, almonds, and cherries. Honey bees alone contribute over $20 billion to the annual value of the U.S. agricultural industry.

Quantity versus Quality: You Decide
While some hemp growers choose to cut corners in favor of larger yields and cheaper overhead, Cannaflower strives to give our customers boutique-grade hemp products. That’s why we strictly adhere to organic practices when we grow both our sun-grown hemp and our premium indoor high-CBD hemp flowers. We also send each batch of our flowers for vigorous third-party lab-testing to ensure that we’re giving you the purest and most potent hemp products possible.
If you would like to know more about our organic farming methods, please contact us at Cannaflower.
Explore Our Menu!
The world’s best CBD hemp flower straight to your door.
Resources
- McMinimy, M. (2019) “The 2018 Farm Bill: Summary and Side by Side Comparison.” Congressional Research Service.
- McEvoy, M. (2019) “Organic 101: What the USDA Organic Label Means.” United States Department of Agriculture.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (2020) “Organic Regulations.” Agricultural Marketing Service.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (2020) “The National List of Allowed and Prohibited Substances.” Agricultural Marketing Service.
- OMRI (2020) “What We Do.” Organic Materials Research Institute.
- Cascardi, L. (2012) “Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as a Phytoremediator.” Colorado State University.
- O’Brien, C. (2018) “What is with All the Buzzing? Exploring Bee Diversity in Industrial Hemp.” Colorado State University.
- American Beekeeping Federation (2020) “Pollination Facts: Honey Bees Are Pollinators.” American Beekeeping Federation.




